


Understanding Return on Equity (ROE): A Comprehensive Guide by AGSSL
Return on Equity (ROE) is a fundamental financial metric that evaluates a company’s profitability by measuring how much return is generated from shareholders’ investment. It indicates how efficiently a company is using the shareholders’ money to generate profits.
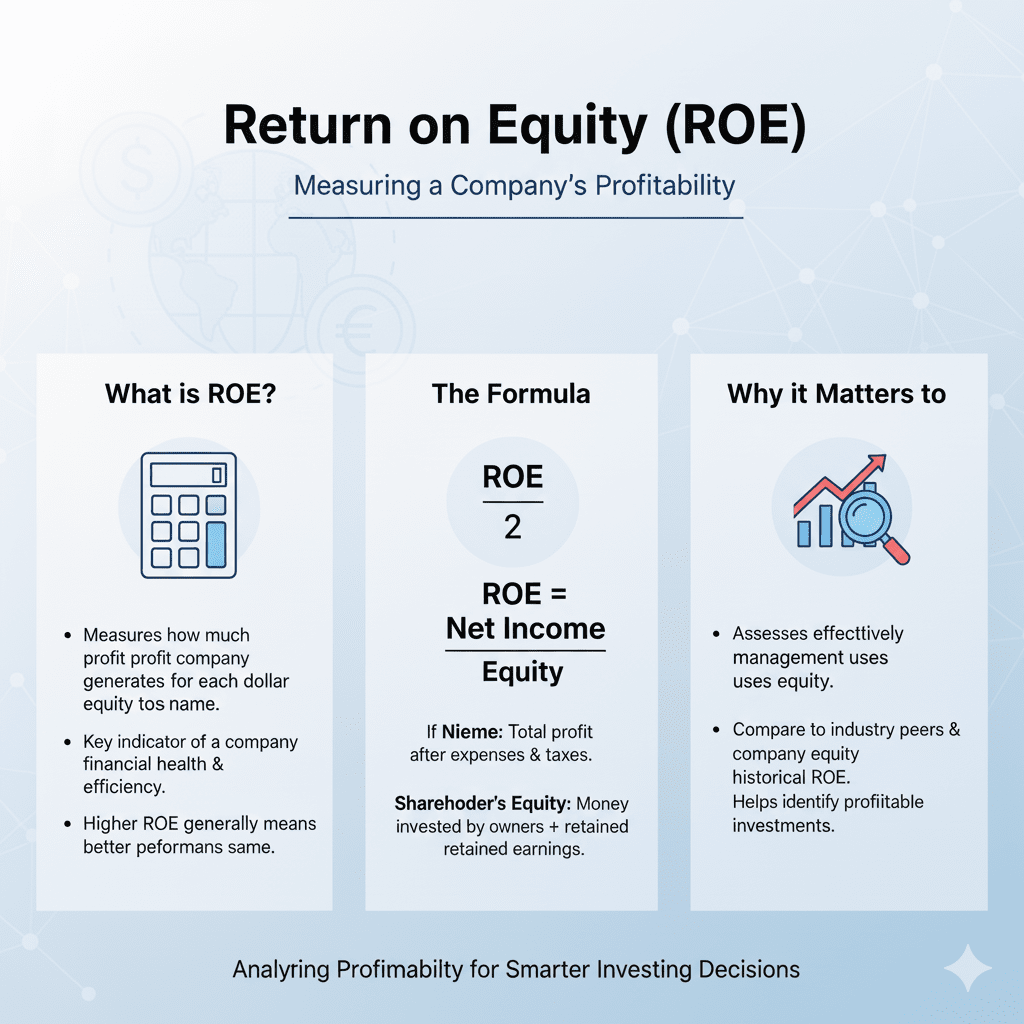
What is ROE?
ROE is calculated by dividing a company’s net profit by its net worth (also known as shareholders’ equity):
ROE = Net Income / Shareholders’ Equity
A high ROE indicates effective use of shareholder capital, while a low ROE suggests that the company is not efficiently utilizing its capital.
Generally, a company with ROE above 20% is considered a good investment.
Why Is ROE Important?
ROE is one of the key indicators used to assess a company’s financial health and profitability. Here’s why it's crucial:
Note: ROE should not be the sole parameter for investment decisions. It can be influenced by financial strategies like debt financing, which may artificially inflate the ROE.
How to Calculate ROE?
To calculate ROE:
ROE = Net Income / Shareholders’ Equity
Analysts often use trailing twelve months (TTM) income for a more accurate calculation. In some cases, free cash flow may be used instead of net income, although net income is more widely accepted.
Why Studying ROE is Significant
1. Represents Financial Soundness
A higher ROE often reflects better financial health and efficient management.
2. Analyzes Company’s Financial Growth
By comparing ROE over different time periods, investors can evaluate how consistently a company has grown.
3. Helps in Peer Comparison
ROE is effective in comparing companies within the same industry. Every sector has a benchmark ROE—comparing a company’s ROE with its industry average helps judge its competitive standing.
4. Gauges Company’s Growth
ROE trends reveal how well a company has used retained earnings to grow profits and shareholder value over time.
5. Detects Financial Irregularities
Drastic changes in ROE, especially spikes after periods of loss, may indicate inconsistencies or one-off events impacting earnings.
What High ROE Tells You
How to Use ROE
1. Estimate Sustainable Growth
Use ROE alongside the retention ratio to estimate a company’s future growth and dividend potential.
2. Evaluate Dividend Capability
High ROE suggests a company can afford consistent and potentially increasing dividend payouts.
3. Apply the DuPont Formula
The DuPont formula breaks ROE into three components:
ROE = (Net Profit Margin) × (Asset Turnover) × (Equity Multiplier)
= (Net Income / Sales) × (Sales / Assets) × (Assets / Equity)
This helps investors understand why ROE is high or low—whether it's due to profit margin, efficient asset use, or leverage.
Can ROE Be Negative?
Yes, ROE can be negative when:
Negative ROE isn’t always a red flag—it could reflect short-term investments or development phases. However, it requires cautious analysis as it might also indicate poor financial management or high debt burden.
Key Takeaways
Final Thoughts from AGSSL
At AGSSL, we encourage investors to make informed decisions by using robust financial tools like ROE—but never in isolation. Combine data with industry trends, company fundamentals, and risk assessments for the best results.
Understanding ROE is a step toward identifying financially sound companies with long-term wealth-generating potential.
Let me know if you'd like this formatted for your website (HTML/Markdown) or want to include charts, case studies, or sector-specific examples.